Last modified 2025-10-28 |
Use the Cache Files SDK Method (Tutorial)
 | Abbreviations Key |
| HISE | Human Immune System Explorer |
hp | hisepy |
| IDE | integrated development environment |
| SDK | software development kit |
pd | pandas |
| UUID | universally unique ID |
At a Glance
This document explains how to use cache_files() (Python) or cacheFiles (R) to download HISE files and store them in your IDE’s cache directory. If you have questions, contact Support.
Method signature
 cache_files()
cache_files()
hp.cache_files(
file_ids: list = None,
query_id: list = None,
query_dict: dict = None,
)
 cacheFiles()
cacheFiles()
cacheFiles( fileIds = NULL, queryId = NULL, query = NULL )
Parameters
The parameters for this method are listed in the following table. In each key:value pair, the value must be of type list.
Python Parameters | ||||||
| Parameter | Data type | Default | Description | |||
file_ids | list | None | List of file IDs | |||
query_id | list | None | List of a single query ID | |||
query_dict | dict | None | Dictionary that allows users to submit a query | |||
R Parameters | ||||
| Parameter | Default | Description | ||
fileIds | NULL | List of UUIDs to retrieve | ||
queryId | NULL | UUID from an advanced search | ||
query | NULL | List of query params to search for. The format is similar to that passed to getFileDescriptors, but the fields correspond to fields in the Subject materialized view. NOTE: fileType with a valid entry must be present | ||
Description
This function downloads HISE files and stores them in your IDE’s cache directory when you pass in one of the following:
- A list of file IDs (Python:
file_ids| R:fileIds) - A saved search ID (
query_id| R:queryId) - A custom search query (
query_dict| R:query)
Unlike read_files, the cache_files method doesn't load files into memory. Instead, it makes them locally available and returns a list of file paths (strings) indicating where each file was downloaded in your local cache directory. Files are downloaded to your IDE's /input directory. The exact paths are returned by the function.
Logging and error handling
For transparency and reproducibility, cache_files automatically logs downloaded file IDs and sample IDs. If a file fails to download, an error message is printed to the console (e.g., "Error downloading file: <error message>"), and the function continues to process the remaining files. Failed file downloads are logged but don't interrupt the caching operation.

Instructions
The following instructions are written for Python. To adapt them for R, use the R function signature and parameters listed above.
 Import libraries
Import libraries
To get started, set up your environment to interact with HISE programmatically and access all available SDK functions. For details, see Use Hise SDK Methods and Get Help in the IDE.
1. Navigate to HISE, and use your organizational email address to sign in.
2. Open an IDE. For instructions, see Create Your First HISE IDE (Tutorial).
3. For programmatic access to HISE functions and efficient handling of tabular data, import the Python SDK and the pandas library.
# Import hisepy and pandasimport hisepy as hp
import pandas as pd
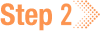 Define file IDs
Define file IDs
In this step, we define the file IDs for this notebook. For details, see Use Advanced Search (Tutorial).
1. Retrieve your own set of file IDs, and then define them as shown below. (The example below uses placeholder UUIDs—replace them with your own.)
# Define the file IDs used in this analysis
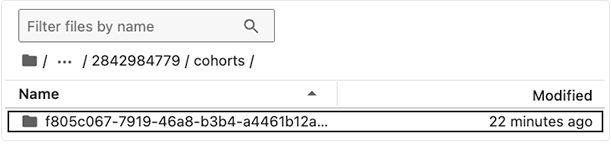
FILEIDS = ['f805c067-7919-46a8-b3b4-a4461b12a279']
 Download files to your cache
Download files to your cache
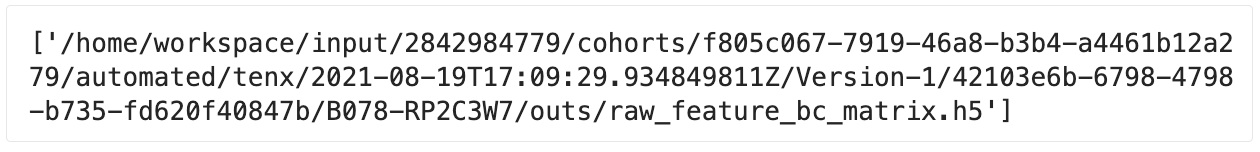
1. To download the file(s) and store them in your local directory, pass in the list of file IDs.
# Cache files locally by file ID
hp.cache_files(file_ids=FILEIDS)
The following output is returned.
 Verify the cache operation (optional)
Verify the cache operation (optional)
1. To can confirm that the cache_files operation was successful, inspect your local HISE cache directory to see the downloaded files. Cached files are stored in /input and organized under subdirectories by dataset, file type, and file ID. The actual file contents are inside the <file_id> directory:
/input/<workspace_path>/<dataset_or_project_id>/<file-type>/<file_id>
 Related Resources
Related Resources