Last modified 2026-01-21 |
Understand Advanced Search Concepts
 | Abbreviations Key |
| HISE | Human Immune System Explorer |
| IDE | integrated development environment |
At a Glance
Advanced Search is the best way to explore files, subjects, and samples in HISE. Its filter-driven interface is designed for research workflows in which you need to find an item–like a set of files or a cohort–that meets several criteria. Define the population and variables of interest to you to curate a well-defined data set. Then hand off the results to visualization, statistical, or pipeline tools for further analysis.
For details, see the Related Resources on this page. If you have questions or need help, contact Support.
Description
Performing complex searches in the redesigned HISE Advanced Search interface is as easy as buying a pair of shoes online. First you pick a category—but instead of flats, slippers, or sneakers, you choose files, samples, or subjects as your search type. Then, instead of color, size, and brand, you use filters like project, assay, age, gender, timepoint, lab results, survey responses, or other metadata to generate a precise set of results. You start with the full universe of available records and progressively pare them down by applying these logical, human-readable filters. Each filter corresponds to a known, structured element in the underlying HISE schema. As you apply each additional filter, even more granular, context-specific options appear. Matching items are displayed in the results window.
Workflow
 Advanced Search underpins several common research workflows, including assembling cohorts of subjects, selecting samples for analysis, and identifying files or reports to add to a study. Because filters are expressed in terms that match scientific and operational concepts, you can refine your queries until the results match your study design. When you have the results you want, you can move them into other parts of HISE. For example, you can save them within specific studies, create new file sets, or launch visualizations for exploratory analysis. Another option is to use an SDK method in R or Python to read or cache the files from an advanced search into your IDE. The typical pattern is shown in the accompanying image. For reproducibility, treat the saved queries themselves as research assets that document how a particular cohort or dataset was defined.
Advanced Search underpins several common research workflows, including assembling cohorts of subjects, selecting samples for analysis, and identifying files or reports to add to a study. Because filters are expressed in terms that match scientific and operational concepts, you can refine your queries until the results match your study design. When you have the results you want, you can move them into other parts of HISE. For example, you can save them within specific studies, create new file sets, or launch visualizations for exploratory analysis. Another option is to use an SDK method in R or Python to read or cache the files from an advanced search into your IDE. The typical pattern is shown in the accompanying image. For reproducibility, treat the saved queries themselves as research assets that document how a particular cohort or dataset was defined.
Best Practices
Advanced Search connects HISE data to specific analysis tools. Use it to carve out the slice of data you want to work with before you create a study or perform an IDE analysis. To define a query, choose a search type (file, samples, or subjects), a project scope, and a set of filters. Start with a broad scope and minimal filters. Then gradually apply additional criteria to narrow your results.
Query IDsUse file IDs, sample IDs, or other explicit identifiers in Advanced Search instead of relying on a query ID parameter and SDK method. We maintain the query ID parameter for backward compatibility. It's deprecated for new workflows, however, because explicit IDs and filter definitions are clearer and easier to reproduce over time. |
Scope
Every search runs within one or more projects, so project selection defines the scope of data you can see and filter. Within that pool, you choose files, samples, or subjects as your search type. This category selection determines which filters are displayed.
Page Organization
The Advanced Search page has four main parts: a header, a sidebar, a results window, and a control (such as a button) to apply your selected filter and update your search results.
 Header
Header
The page header shows where you are within Advanced Search and lets you return to a previous level in the navigation path. It includes breadcrumb links and navigation controls, such as the BACK button shown here.

 Sidebar
Sidebar
The left sidebar organizes filters into three search types: FILES, SAMPLES, and SUBJECTS. Within each of these tabs, filters are grouped into logical categories, such as file metadata, sample metadata, subject metadata, lab results, surveys, and custom metadata. These filters reflect how HISE organizes your data. They help you translate domain questions (for example, subjects with a particular assay result) into structured searches.
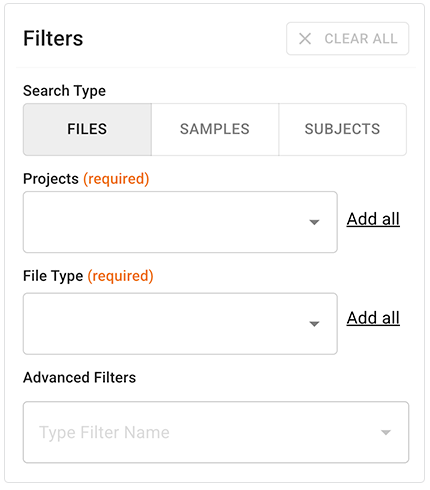
 Results window
Results window
The results area to the right of the filters shows matches in a tabular format. Table columns are context specific, depending on your search type and filter selections. To reduce clutter, table controls, such as column menus, appear only when you hover over them. For more options, click the ellipsis next to any table column heading. Select the columns displayed in the results window, hide columns to create a more compact view, filter the results, or resort the columns (for example, reorder batch IDs from descending to ascending).
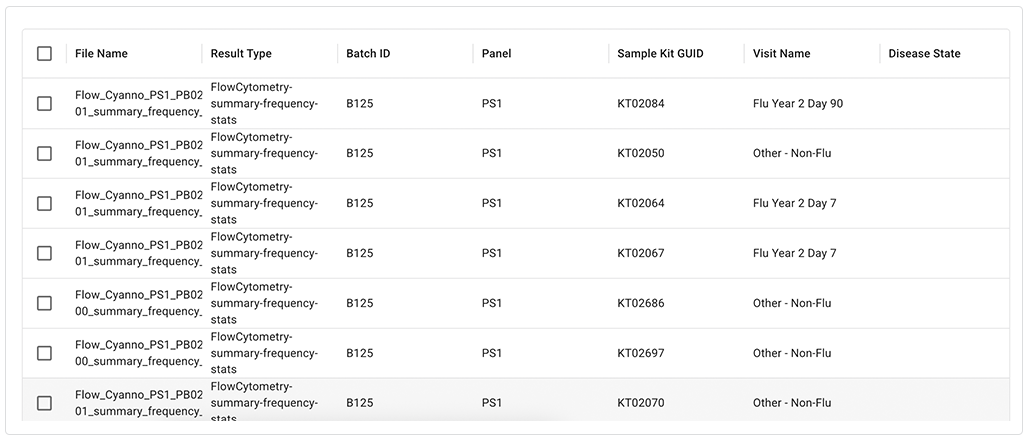
 Controls
Controls
Available controls are context specific. See the accompanying table for a list of typical controls and their types, functions, and locations.
Context-Specific Page Controls | ||||
| Control | Type | Function | Location | |
 | ACTIONS | Button with drop-down menu | Opens a menu of additional actions you can perform on the currently selected results, such as adding items to file sets, getting scripts, or visualizing data. | Upper-right corner of results window |
 | VIEW SAVED & SHARED | Button | Opens a panel in which you can view, load, and manage saved and shared Advanced Search queries. | Upper-right corner of results window |
 | CLEAR ALL | Button | Clears all active filters in the filters sidebar and resets the results to the unfiltered state. | Filters sidebar |
 | SELECT ALL ITEMS | Button | Selects all items currently shown in the results window. | Upper-left corner of results window, near middle of screen |
 | CLEAR SELECTION | Button | Deselects all items currently selected in the results window. | Upper-left corner of results window, near middle of screen |
 | APPLY | Button | Applies your filter selections or other choices. | Dialog box |
 | CANCEL | Button | Cancels your filter selections or other choices and closes the dialog box. | Dialog box |
Saved & Shared Queries
All queries begin as unsaved, temporary queries that exist only as long as the current browser state persists. They're lost if you refresh or navigate away from the page. On the Saved & Shared Queries page, you can see all the queries you or your collaborators have saved. To learn how to save a query, see Use Advanced Search for Basic Queries (Tutorial).
Saved queries have varying visibility levels, as shown in the accompanying table. These visibility settings determine who can find and run a query, but they don't change the underlying data permissions on the projects the query represents.
Query Visibility | |||
| Visibility type | Visibility level | Description | |
 | Your Private Queries | Private to you | Only you can see and run the saved query in HISE. It doesn't appear in the Saved & Shared Queries list of any other user, even if they have access to the same projects or data. |
 | Queries Shared With You | Shared with specified collaborators | Saved queries visible to the specified set of users or groups. Those collaborators can see and run the query. They might also edit or manage it, depending on their permissions, but the query is hidden from everyone else on the account. |
 | Queries You Have Shared | Available either to specified users or to everyone, depending on your selection | Saved queries that you created and explicitly shared. |
 | Queries Shared With All Users In Account | Available to all HISE users who have permission to view the specified projects | Saved queries that any allowed user can run. The right to edit or manage the query (for example, to delete it) follows the usual role-based permissions model. |
A saved query entry, such as the one in this example, displays some or all the key details outlined in the accompanying table.
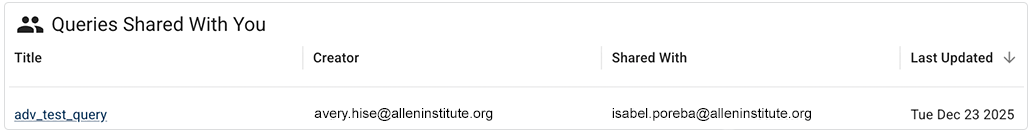
| Category | Each query appears in a section that indicates its visibility, such as Queries Shared with You. The preceding example shows a query that's shared with specified collaborators, including the current user. |
| Title | Descriptive title the user selected when saving the query. |
| Creator | Name of the user who built and saved the query. |
| Shared With | Name(s) of the user(s) the query is shared with. |
| Last Updated | Date on which the query was last modified by the creator or another user. |
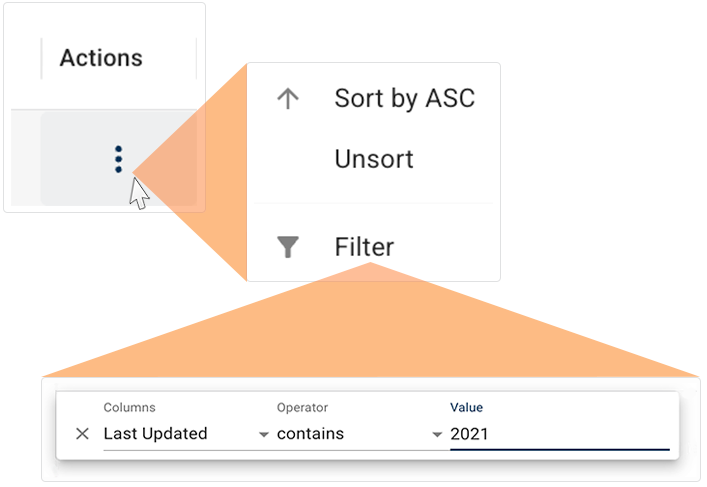
To sort saved queries in ascending or descending order by date, click the Last Updated column head.

For more filtering options, click the ellipsis in the Actions column next to any saved query.
 Related Resources
Related Resources
Use Advanced Search for Basic Queries (Tutorial)
Use Advanced Filters for Complex Searches (Tutorial)